(5)数据结构与算法
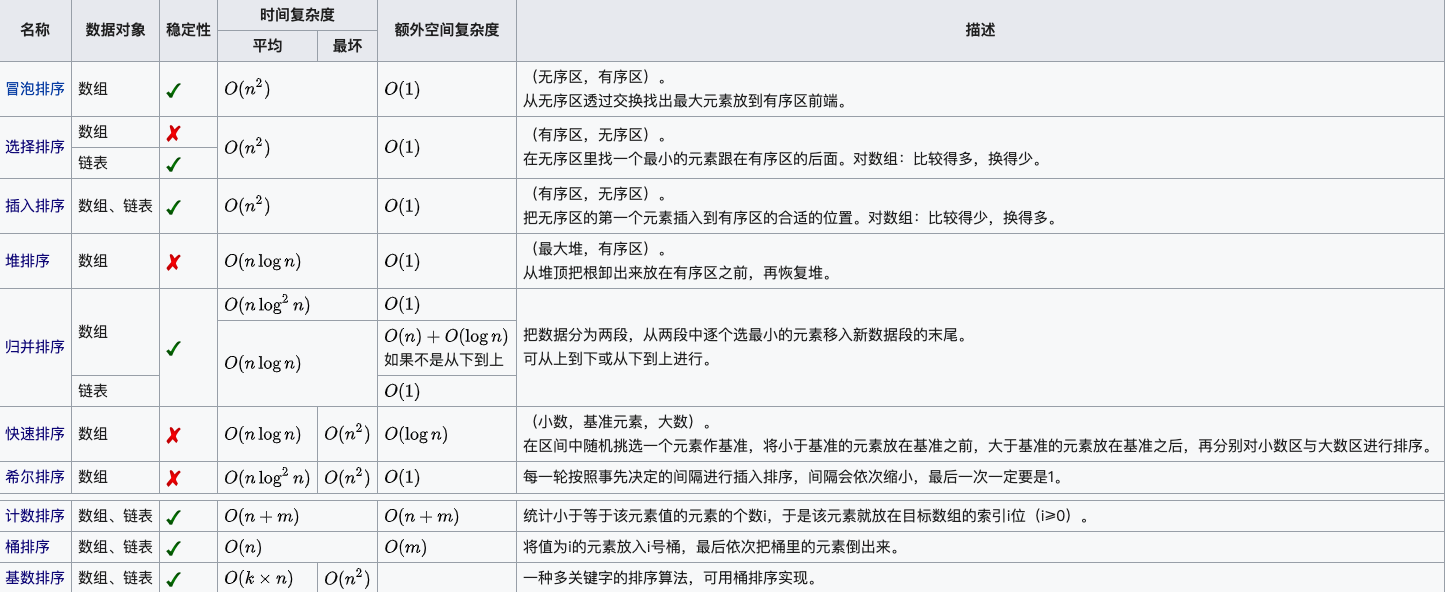
1 说说常见的排序算法和复杂度?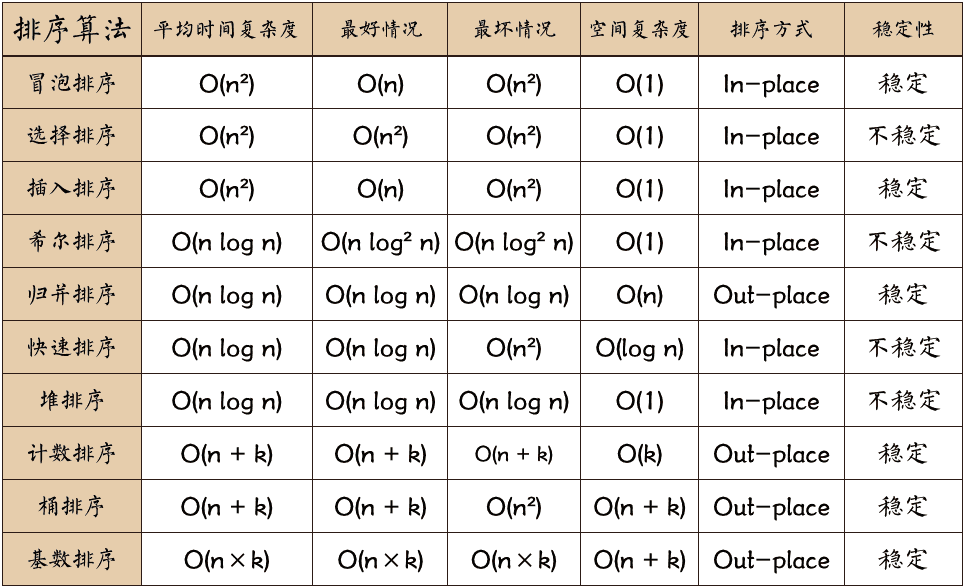
2 如何实现一个冒泡排序算法?
冒泡排序的基本思想是:通过对待排序序列从前向后(从下标较小的元素开始),依次比较相邻元素的值,若发现逆序则交换,使值较大的元素逐渐从前移向后部,就象水底下的气泡一样逐渐向上冒。假设数组长度为n,冒泡排序共执行n-1次排序,在第i次排序中对从第一个元素到第n-i个元素进行两两遍历,如果右边小于左边则进行交换。
public static void BubbleSort(int[] arr){
// 临时变量
int temp;
// 表示趟数,一共arr.length-1次
for(int i=0; i<arr.length-1; i++){
for(int j=arr.length-1; j>i; j--){
if(arr[j] < arr[j-1]){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
arr[j-1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
3 如何遍历一棵二叉树?
二叉树的遍历就是将二叉树中的所有节点遍历打印出来。经典的方法有三种,前序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历。前、中、后是根据节点被打印的先后来进行区分的:前序就是先打印节点本身,之后再打印它的左子树,最后打印它的右子树;中序就是先打印节点的左子树,再打印节点本身,最后打印右子树,即把节点放中间的位置输出;后序就是先打印节点的左子树,再打印节点的右子树,最后打印节点本身。如下图所示: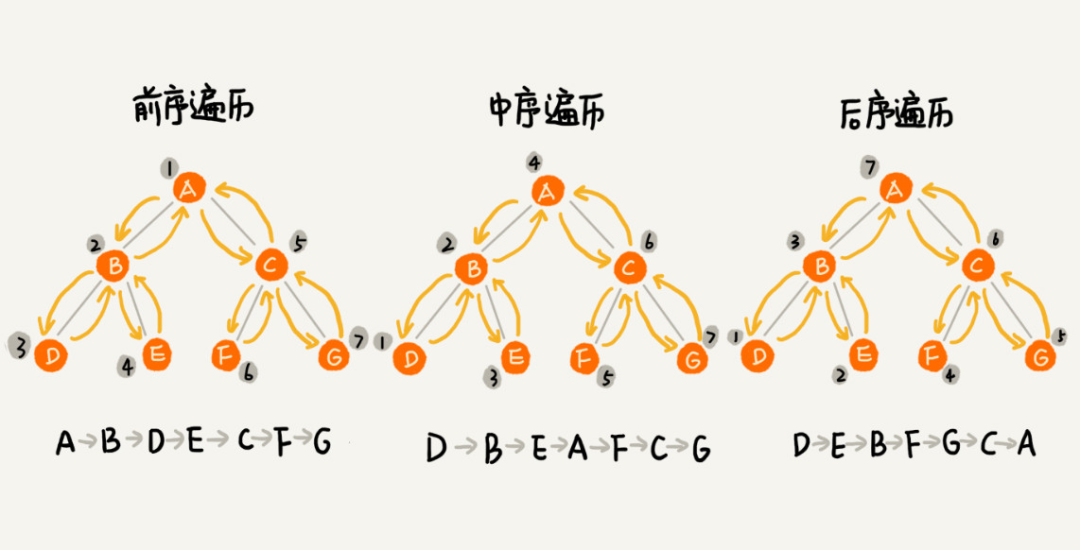
代码实现如下:
import java.util.Stack;
public class BinTreeTraversal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("前序:");
Traversal.preOrder();
Traversal.preOrderRecursion(Traversal.createBinTree());
System.out.print("中序:");
Traversal.inOrder();
Traversal.inOrderRecursion(Traversal.createBinTree());
System.out.print("后序:");
Traversal.postOrder();
Traversal.postOrderRecursion(Traversal.createBinTree());
}
}
/**
* 节点数据结构
*
*/
class BinTreeNode {
BinTreeNode() {
}
BinTreeNode(char data, int flag, BinTreeNode lchild, BinTreeNode rchild) {
this.data = data;
this.flag = flag;
this.lchild = lchild;
this.rchild = rchild;
}
char data;
int flag;
BinTreeNode lchild, rchild;
}
class Traversal {
/**
* 创建一棵二叉树
*
*/
public static BinTreeNode createBinTree() {
BinTreeNode R3 = new BinTreeNode('F', 0, null, null);
BinTreeNode L2 = new BinTreeNode('D', 0, null, null);
BinTreeNode R2 = new BinTreeNode('E', 0, null, R3);
BinTreeNode L1 = new BinTreeNode('B', 0, L2, R2);
BinTreeNode R1 = new BinTreeNode('C', 0, null, null);
BinTreeNode T = new BinTreeNode('A', 0, L1, R1);
return T;
}
// 前序
public static void preOrder() {
BinTreeNode p = createBinTree();
Stack<BinTreeNode> stack = new Stack<BinTreeNode>();
while (p != null || !stack.empty()) {
if (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.data);
stack.push(p);
p = p.lchild;
} else {
p = stack.pop();
p = p.rchild;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// 前序递归
public static void preOrderRecursion(BinTreeNode top) {
if (top != null) {
System.out.println(top.data);
preOrderRecursion(top.lchild);
preOrderRecursion(top.rchild);
}
}
// 中序
public static void inOrder() {
BinTreeNode p = createBinTree();
Stack<BinTreeNode> stack = new Stack<BinTreeNode>();
while (p != null || !stack.empty()) {
if (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.lchild;
} else {
p = stack.pop();
System.out.print(p.data);
p = p.rchild;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// 中序递归
public static void inOrderRecursion(BinTreeNode top) {
if (top != null) {
inOrderRecursion(top.lchild);
System.out.println(top.data);
inOrderRecursion(top.rchild);
}
}
// 后序
public static void postOrder() {
BinTreeNode p = createBinTree();
Stack<BinTreeNode> stack = new Stack<BinTreeNode>();
// 初始化栈
int mark = 1;
// 转向标志
while (p != null || !stack.empty()) {
// 遍历
if (p != null && mark != 0) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.lchild;
}
// 转向左子树 else {
p = stack.pop();
p.flag++;
// 退栈
if (p.flag == 1) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.rchild;
mark = 1;
}
// 转向右子树 else if (p.flag == 2 && !stack.empty()) {
// 输出结点
System.out.print(p.data);
mark = 0;
} else if (p.flag == 2 && stack.empty()) {
// 输出根结点并退出
System.out.print(p.data);
break;
}
}
// if-else
}
// while
System.out.println();
}
// 后序递归
public static void postOrderRecursion(BinTreeNode top) {
if (top != null) {
postOrderRecursion(top.lchild);
postOrderRecursion(top.rchild);
System.out.println(top.data);
}
}
}
4 如何倒排链表?
如果单向链表的内容是: a -> b -> c ->d,倒排就是 d -> c -> b -> a 。首先定义节点:
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
迭代反转链表:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy.next;
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode then = start.next;
while (then != null) {
start.next = then.next;
then.next = pre.next;
pre.next = then;
then = start.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
递归反转链表:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){
if (head.next == null || head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode nextNode = head.next;
ListNode last = reverseList(nextNode);
nextNode.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
5 如何递归遍历目录下面所有文件?
public static void ScanFiles(File file) {
if (file == null || !file.exists()) {
return;
}
if (!file.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println(file.getName());
} else {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
if (files != null) {
for (File f : files) {
ScanFiles(f);
}
}
}
}
6 描述一下链式存储结构,并用代码实现双向链表?
链式存储结构的元素在物理内存上的分配是随机的,可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的,每一个存储单元分为两部分数据域(Object)和指针域(引用)。常见的链式存储结构有单向链表和双向链表。链表的结构特点就是有一个值字段,同时有指向下一个结点或者上一个结点的字段,代码定义如下:
//单向链表
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
}
//双向链表
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode pre;
ListNode next;
}
查找:由于元素之间是不连续的,所以只能从头节点通过指针进行元素的查找,时间复杂度为O(n)。
修改:修改和查找一样,找到直接替换即可,时间复杂度为O(n)。
插入:元素的插入只需要断开插入位置的指针,并将插入位置的前元素的指针域指向新加入的元素,将新加入的元素的指针指向插入位置前元素的指针所指向的元素即可,时间复杂度为O(1)。
删除:和插入的情况相同。
双向链表代码实现如下:
public class DuLinkList<T> {
/**
* 内部类:链表中的一个节点
*
* @author liuhao data 节点中的数据 prev 指向前一个节点的引用 next 指向下一个节点的引用
*/
private class Node {
private T data;
// 保存的数据元素
private Node prev;
// 指向上一个节点
private Node next;
// 指向下一个节点
public Node() {
}
public Node(T data, Node prev, Node next) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.prev = prev;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node header;
// 头结点
private Node tail;
// 尾节点
private int size;
// 链表中元素个数
// 创建空链表
public DuLinkList() {
header = null;
tail = null;
}
// 已指定数据元素创建链表,只有一个元素
public DuLinkList(T element) {
header = new Node(element, null, null);
// 只有一个节点,header,tail都指向该节点
tail = header;
size++;
}
// 返回链表长度
public int length() {
return size;
}
// 获取指定位置的数据元素
public T get(int index) {
return this.getNodeByIndex(index).data;
}
// 获取指定位置的节点
private Node getNodeByIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引超出线性表范围");
}
if (index < size / 2) {
Node current = header;
for (int i = 0; i < size / 2 && current != null; i++, current = current.next) {
if (i == index) {
return current;
}
}
} else {
Node current = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i >= size / 2 && current != null; i--, current = current.prev) {
if (i == index) {
return current;
}
}
}
return null;
}
// 按值查询所在的位置
public int locate(T element) {
Node current = header;
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1 && current != null; i++, current = current.next) {
if (element.equals(current.data)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 向指定位置插入元素
public void insert(T element, int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引超出线性表范围");
}
if (header == null) {
this.add(element);
} else {
if (0 == index) {
this.addAtHead(element);
} else {
Node prev = this.getNodeByIndex(index - 1);
// 获取插入节点的前一个节点
Node next = prev.next;
// 待插索引处的节点
Node newNode = new Node(element, prev, next);
// 新增节点,让它的prev指向之前的节点。next指向之后的节点
prev.next = newNode;
// 之前的节点的next指向当前节点
next.prev = newNode;
// 之后节点的prev指向当前节点
size++;
}
}
}
// 采用尾插法添加新节点
public void add(T element) {
// 若还是空表,则将header和tail都指向该元素即可
if (header == null) {
header = new Node(element, null, null);
tail = header;
} else {
// 创建信节点,prev指向tail
Node newNode = new Node(element, tail, null);
// 令tail的next指向新节点
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
// 把新节点设为尾节点
}
size++;
}
// 采用头插发添加新节点
public void addAtHead(T element) {
Node newNode = new Node(element, null, header);
header.prev = newNode;
header = newNode;
// 如果插入之前是空表
if (tail == null) {
tail = header;
}
size++;
}
// 删除指定索引处的元素
public T delete(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引超出线性表范围");
}
Node del = null;
if (index == 0) {
del = header;
header = header.next;
header.prev = null;
} else {
Node prev = this.getNodeByIndex(index - 1);
// 获取索引处之前的节点
del = prev.next;
// 获取索引处的节点
// 让之前的节点的next指向下一个节点
prev.next = del.next;
// 有可能删除的是最后一个元素,若直接调用next.prev可能会出错
if (del.next != null) {
del.next.prev = prev;
}
//若删除的是最后一个元素,那么就要重置tail;
tail = prev;
del.prev = null;
del.next = null;
}
size--;
return del.data;
}
// 删除最后一个元素
public T remove() {
return this.delete(size - 1);
}
// 判断是否为空
public Boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 清空线性表
public void clear() {
header = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
public String toString() {
if (size == 0) {
return "[]";
} else {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
for (Node current = header; current != null; current = current.next) {
sb.append(current.data.toString() + ", ");
}
sb.append("]");
int len = sb.length();
// 删除多余的“,”和空格
return sb.delete(len - 3, len - 2).toString();
}
}
}
测试双向链表:
public class DuLinkListTest {
public void test() {
//测试构造函数
DuLinkList<String> duList = new DuLinkList("好");
System.out.println(duList);
//测试添加元素
duList.add("ni");
duList.add("没");
System.out.println(duList);
//在头部添加
duList.addAtHead("五月");
System.out.println(duList);
//在指定位置添加
duList.insert("摩卡", 2);
System.out.println(duList);
//获取指定位置处的元素
System.out.println("第2个元素是(从0开始计数):" + duList.get(2));
//返回元素索引
System.out.println("摩卡在的位置是:" + duList.locate("摩卡"));
System.out.println("moka所在的位置:" + duList.locate("moka"));
//获取长度
System.out.println("当前线性表的长度:" + duList.length());
//判断是否为空
System.out.println(duList.isEmpty());
//删除最后一个元素
duList.remove();
System.out.println("调用remove()后:" + duList);
//获取长度
System.out.println("当前线性表的长度:" + duList.length());
//删除指定位置处元素
duList.delete(3);
System.out.println("删除第4个元素后:" + duList);
//获取长度
System.out.println("当前线性表的长度:" + duList.length());
//清空
duList.clear();
System.out.println(duList);
//判断是否为空
System.out.println(duList.isEmpty());
}
}
